Summary:
- This section they talk about how enzymes speed up chemical reactions in different cells. By either lowering the activation energy or from other catalysts.
- Activation energy is the needed energy that is absorbed by molecules to start a reaction. The reaction are usually endothermic.
- But when heating up a cell too much can destroy them so that is what catalysts do, they lower the needed energy so then the cell can still live and achieve the reaction.
- Human catalyst that are used in many things in the body are known as enzymes, our body reproduces them.
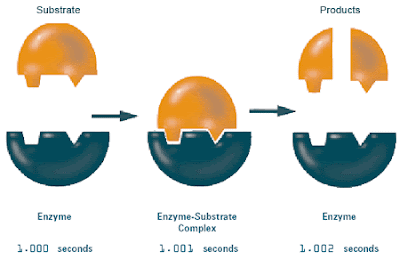
- A enzymes works by using a reactant known as the substrate, they are to fit into the region of the enzyme known as the active sight. Afterwards it weakens the substrates bond and when the water molecule is introduced, they convert or break down the substrate into different molecules.
- Other than the normal things, enzymes can be highly affected by ph levels and temperature.
Concept Check
1. Explain the role of activation energy in a reaction. How does an enzyme affect the activation energy?
The activation energy is the energy needed to get the reaction starting and the enzyme can decrease the amount of energy needed to start.
2. Describe how a substrate interacts with an enzyme.
First the substrate fits into the enzyme's active site and it binds them together, later when water is introduced the enzyme with break down the substrate.

No comments:
Post a Comment