Summary
- This section is about the use of proteins and where they contribute to the body.
- Protein is a polymer that is made from a set of 20 different kinds of monomers that are known as amino acids. Proteins are what makes us able to do what we do everyday, hair and muscle are made protein. Proteins that cannot be seen are found circulating the blood stream protecting the body from microorganisms.
- Every amino acid monomer contains a middle carbon atom that is bonded to four other covalent bonds. Three partners of the carbon atom are the same in all amino acids, they are the hydrogen atom, two are a carboxyl group and the other is an amino group.
- The thing that differs from every amino acid is their side group or is known also known as the R-group. They are responsible for the different chemical properties of the amino acid.
- Proteins are made by linking the amino acids into a chain called polypeptide, every link is created by the dehydration reaction, proteins needs at least one or more polpeptides. There are many variety of proteins because of different formulas of amino acids formed together.
- Proteins look like a clump of cells wrapped together into a unique shape, and protein has to be in the exact same shape and size to become the same protein. Shapes of the protein can also be altered by their surrounding enviroment. If the protein gets too hot it starts to unravel and loses its ability to function.
Concept Check
1. Give atleast two exmples of protein you can "see" in the world around you. What are their functions?
Hair is one example, hair is used to make people look good and make bald people feel insecure. Egg whites are examples of protein that will give you energy to use.
2. Relate amino acids, polpeptides, and proteins.
Amino acids are basic monomers that are linked together to form a polpeptide. Polpeptides are used to make proteins by folding and twisting together.
3. Explain how heat can destroy a protein.
Heat can destroy a protein because it can unravel the protein not and making the strings of proteins useless and they lose their original ability.
4. Which parts of amino acid's structure are the same in all amino acids? Which part is unique?
The hydrogen atom, carboxyl group and the amino group are always the same in all amino acids. However the side group of an amino acid is always the unique one because it make the amino acid different from all the others.
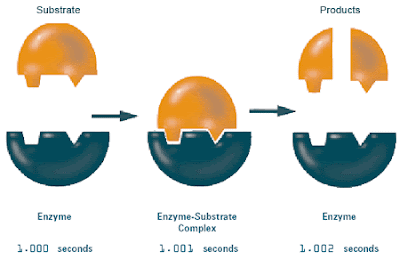
 Protein molecule
Protein molecule